Sommario
At ANY.RUN, we closely monitor the threat landscape around the world, tracking the latest developments in different regions. Our database of publicly submitted samples, which grows by thousands of new entries each day, serves as our ultimate source of data.
In this report, we present the findings of our investigation into the primary malware trends in Europe in Q2 2023.
Summary
| Q2 2023 review Overall uploads in ANY.RUN | |||
| Country | Total | Malicious | Suspicious |
| EU | 148,878 | 58,620 | 6,829 |
| France | 13,095 | 3,509 | 536 |
| Spain | 28,110 | 10,467 | 1,151 |
| Italy | 9,881 | 3,240 | 562 |
| Germany | 40,191 | 23,813 | 1,690 |
In Q2 of 2023, ANY.RUN analyzed a total of 148,878 samples from the EU region. Of these, 58,620 were malicious and 6,829 were suspicious. Users from Germany uploaded the largest number of malware samples, followed by users from France, Spain, and Italy. The most common type of malware was Remote Access Trojan (RAT), while the most prevalent family of malware was RedLine.
Top Malware Types in Europe, Q2 2023
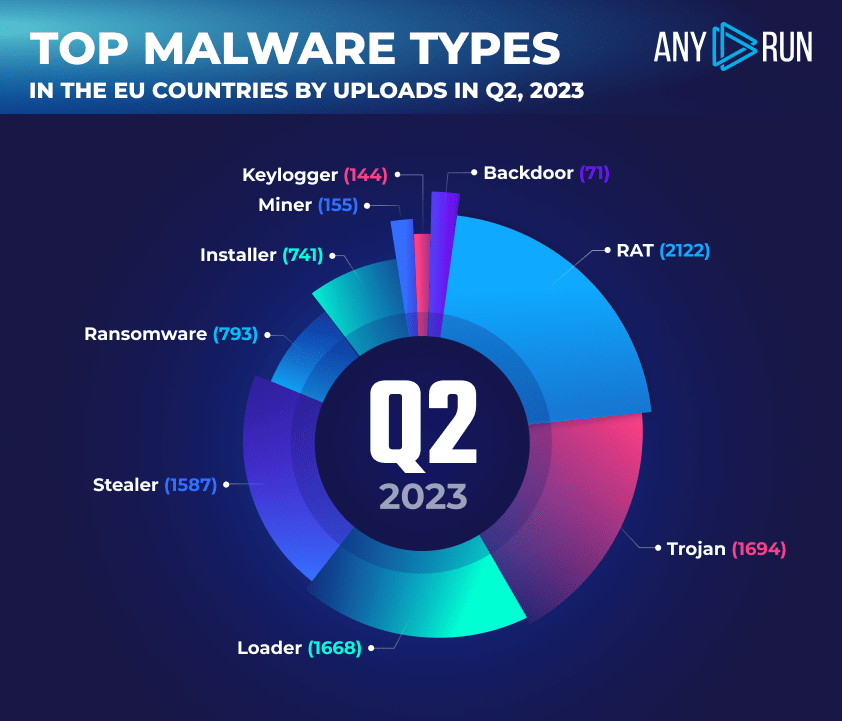
- RATs top the chart: Accounting for 23.64% of all uploads, RATs are a versatile type of malware that can be used for a variety of malicious purposes, which is one of the reasons for their popularity. Check out our full technical breakdown of one of the most recent RAT variants, Gh0stBins.
- Trojans come in second: Disguising themselves as legitimate files, trojans can be hard to detect for someone who is not cybersecuity-savvy. As a result, they continue to be a go-to option for numerous black hats, which is why 18.87% of all uploads in Q2 belonged to this malware type.
- Loaders are ranked third: Loaders, which bypass security measures and install malware that would otherwise be blocked, were found in 18.58% of malware samples. Loaders can be tricky to pin down without advanced tools such as ANY.RUN.
- The malicious four: The top 4 malware types on our list make up over 78% of all malware uploads in the EU. Therefore, analysts are advised to pay particular attention to RATs, trojans, loaders, and stealers.
Top Malware Families in Europe, Q2 2023
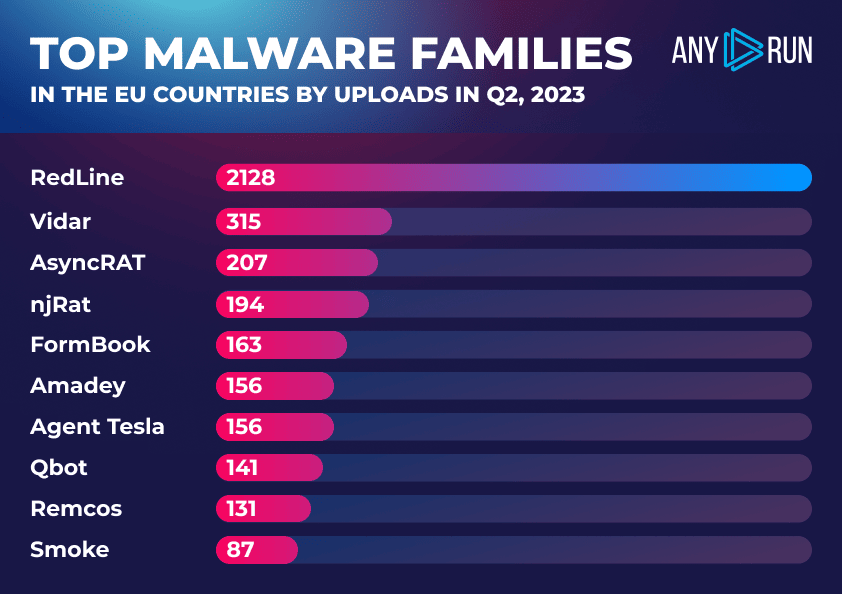
- Top concern: RedLine remains the most prevalent malware in Europe in 2023, being discovered in over half of all uploads. You can explore RedLine’s IOCs and see its latest samples via ANY.RUN’s Tracker.
- Prominent threats: The Vidar trojan has reemerged as one of the most frequently encountered malware, while AsyncRAT and NJRAT, and the Formbook stealer slightly lost their popularity compared to the results from the Q1 2023 global trends report.
- Notable mentions: Amadey, Qbot and AgentTesla still occupy a significant portion of Europe’s cyber threat landscape, while Emotet, despite causing analysts a serious headache, seemingly continues to fall out of favor with hackers.
Key Takeaways
- RATs pose a major risk in Europe. This makes it crucial to prioritize the safeguarding of remote access channels and keep an eye on network activity to prevent any unauthorized access or data theft.
- The four most persistent types of malware, namely RATs, trojans, loaders, and stealers, constitute over 78% of all uploads in the EU. This fact highlights the importance of focusing on understanding the behaviors of these malicious programs.
- For two consecutive quarters, RedLine has retained its top ranking as the most significant malware threat. It works by infiltrating devices through phishing emails, malicious attachments, or drive-by downloads. Once installed, it operates stealthily in the background and can steal sensitive data without alerting the user.
Methodology
As part of our research, we’ve examined data submitted to our public threat database by an international community of researchers, who have opted to make the results of their analysis public.
While this report should not be regarded as an exhaustive representation of the malware threat landscape in Europe, we believe it can provide valuable insights into the most prevalent threats, as observed through the perspective of our sandbox.
Conclusion
Taking proactive measures to counter threats is the best strategy for improving your organization’s cybersecurity posture. ANY.RUN equips you with the capabilities necessary for advanced malware research.

